In comparative static, the problem under consideration is finding the rate of change i.e., the rate of change of the equilibrium value of an endogenous variable with respect to the change in a particular parameter or exogenous variable. The mathematical concept of derivative take an important significance in comparative statics. The concept of derivative is also important for optimisation.
Let us take a function 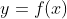 where
where 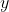 changes in response to changes in variable
changes in response to changes in variable 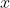 .
.
THE DIFFERENCE QUOTIENT:
When variable 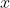 changes from the value
changes from the value 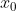 to a new value
to a new value 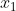 , the change is measured by the difference
, the change is measured by the difference  .
.
Using the symbol ∆ to denote change, we write
When 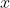 changes from initial value x_o to a new value
changes from initial value x_o to a new value 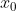 to a new value
to a new value 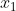 or
or  , (since
, (since  , therefore
, therefore  ), the new value of the function
), the new value of the function 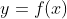 changes from
changes from  to
to  .
.
The change in 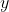 per unit change in
per unit change in 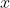 can be represented by the difference quotient.
can be represented by the difference quotient.
This quotient which measures the average rate of change of y , can be calculated if we know the initial value of 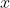 or
or 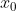 and the magnitude of change in
and the magnitude of change in 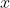 or
or 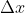 . That is
. That is 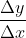 is a function of
is a function of 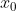 and
and 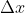 .
.
If 
Then,
Now, the difference quotient is:
which can be evaluated given 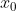 and
and 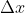 .
.
If 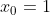 and
and 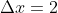 .
.
Then, the average rate of change of 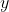 is:
is:
DERIVATION OF THE DERIVATIVE:
In many cases, we are interested in the rate of change of 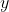 when
when 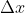 is very small. If the change in
is very small. If the change in 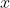 i.e.,
i.e., 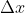 is very small, we can get an approximation of
is very small, we can get an approximation of 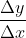 by dropping all the terms in the difference quotient involving the expression
by dropping all the terms in the difference quotient involving the expression 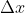 . The smaller the value of
. The smaller the value of 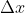 the closer the approximation to the true value of
the closer the approximation to the true value of 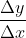 .
.
In  we may take
we may take  as an approximation of
as an approximation of 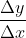 .
.
In case of  , as
, as 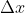 approaches zero (it gets closer and closer to, but never actually reaches zero)
approaches zero (it gets closer and closer to, but never actually reaches zero)  will approach the value
will approach the value  and hence
and hence 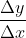 will approach
will approach  also. Symbolically,
also. Symbolically,  .
.
or by equation,
where lim is the limit of the function  as
as 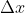 approaches zero.
approaches zero.
If as  , the limit of the difference quotient does exists, the limit is called the derivative of the function
, the limit of the difference quotient does exists, the limit is called the derivative of the function 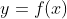 .
.
Hence, the derivative of a given function 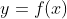 can be written as:
can be written as:
IMPORTANT POINTS:
- A derivative is a function. The word derivative means a derived function. The original function
is a primitive function and derivative is another function derived from it.
- Since the derivative is merely a limit of the difference quotient, which measures a rate of change of
, the derivative must of necessity also be a measure of some rate of change.
- Derivative functions are denoted in two ways:
1. One way of denoting its derivative is to use the symbol 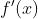 or simply
or simply 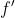 . This notation is attributed to the mathematician Lagrange.
. This notation is attributed to the mathematician Lagrange.
2. Another common notation is 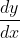 devised by the mathematician Leibniz.
devised by the mathematician Leibniz.


No comments:
Post a Comment